Small Motors: Applications and Required Technology

Small motors are indispensable in today's high-tech society. They are used in a wide range of applications, from critical medical and industrial devices, to everyday home appliances.
When classified by output, motors producing 75W or less are considered small motors, while those generating 3W or less fall into the category of micromotors (also known as ultra compact motor). These motors require minimal power to operate, often running on the equivalent energy of a standard dry-cell battery. In applications where compact size is essential, DC motors are generally preferred over AC motors, as AC motors require high voltages of 100V or more, increasing the risks of electrical leakage and fire.
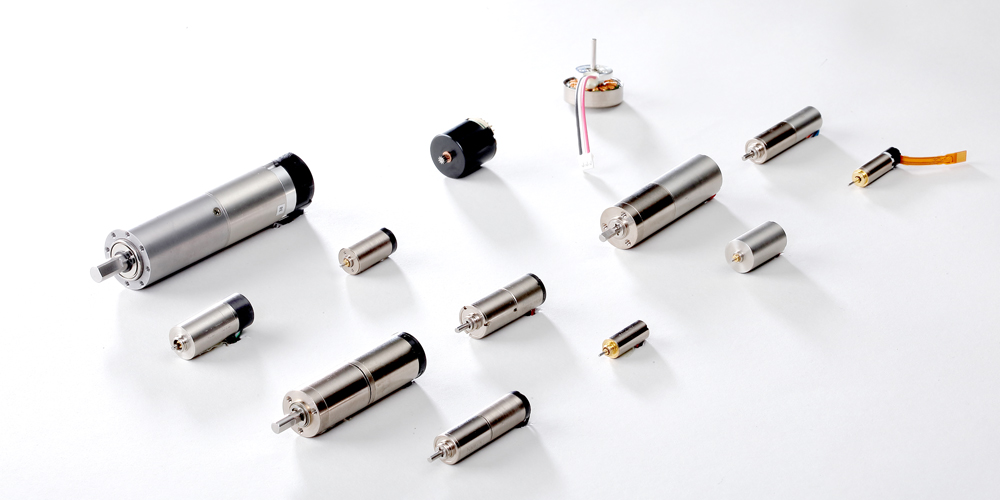

Table of contents [close]
How they work | Rotational motion from electric current
When a magnetic field interacts with an electric current, an electromagnetic force is created. This electromagnetic force is the basis for the operation of all electric motors. Inside the motor, magnets and coils are arranged to harness the fundamental properties of electromagnetism: opposite poles attract, like poles repel. When arranged just right, this results in continuous rotational motion.
Classification by power source and architecture
Very broadly, motors can be categorized based on their power source. AC motors operate on alternating current, and DC motors run on direct current. AC motors are commonly found in large industrial applications, such as pumps and conveyors used in factory equipment. In contrast, DC motors are typically smaller and used in a wide variety of products, including household appliances and electronic devices.
DC motors are further classified into brushed DC motors and brushless DC motors. For small motors, the permanent magnet field method is commonly used, as the magnets allow for a highly efficient and compact design. Orbray’s small motors also use this method, ensuring superior performance in precision applications.
Brushed DC motor case
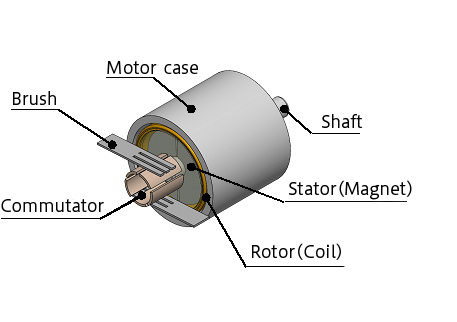
A brushed DC motor consists of a rotor made of a copper wire coil, and a magnetic stator. The end of the coil is connected to the commutator, which creates the contact point. The commutator is able to rotate while maintaining contact with the brush. DC current flows through the brush. When the commutator and the brush come into contact, electricity flows into the coil, creating a magnetic field that either repels or attracts the stator, causing the rotor to rotate. As the rotor rotates, current flowing through the coil alternates between attracting and repelling, keeping the rotor in motion.
One of the key advantages of a brushed DC motor is its simple structure, which enables rotation without the need for a drive circuit. However, because the brushes and commutator are in constant contact, they experience wear over time, requiring periodic brush replacement. Additionally, mechanical and electrical noise can occur due to the friction and sparking at the contact points.
Coreless motors
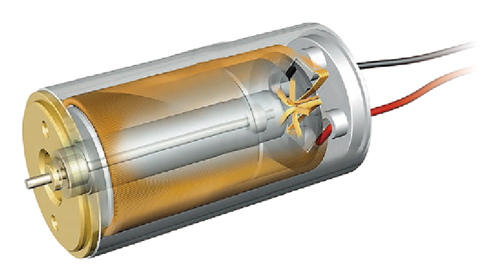
Coreless motors are a type of brushed DC motor designed without a traditional iron core in the rotor. Instead, the coil is wound into a cylindrical, cup-like shape, forming a cage-like rotor that rotates around the magnets placed inside.
By eliminating the core, the rotor becomes lighter, reducing its moment of inertia and allowing for faster startup and improved response time. This design also generates less heat, even at high speeds, enabling efficient rotation. Additionally, coreless motors avoid cogging, the unwanted resistance caused by the attraction between the core and magnet, resulting in smoother rotation with minimal vibration and noise. Orbray's coreless motors are developed using this advanced design, achieving high performance and efficiency for precision applications.
Brushless DC motor case
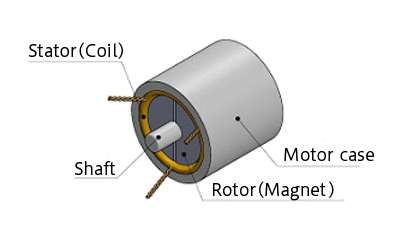
Brushless DC motors operate without brushes and commutators, using a rotor made of magnets and a stator composed of coils. They are designed in one of two configurations: an inner rotor type, where the stator surrounds a centrally placed rotor, or an outer rotor type, where the rotor encases the stator and rotates around it.
Brushless motors can also be categorized by their internal structure as coreless or cored. Orbray primarily develops coreless brushless motors (inner rotor type) but also offers a lineup of cored brushless motors with an outer rotor design for specialized applications.
One of the key advantages of brushless DC motors is that they don’t have electrical contacts, which eliminates the need for maintenance related to contact wear and significantly extends lifespan. Additionally, because there are no electrical contacts, it’s possible to apply large currents for high power output. However, to function, brushless motors require a dedicated drive circuit to control the flow of current to the coils, which adds to overall cost.
Column: Motor applications
Geared motors, which integrate speed reduction mechanisms, are one way to modify the output characteristics of a motor. Gearing lowers rotational speeds while increasing torque, allowing these motors to be used in a broader range of applications.
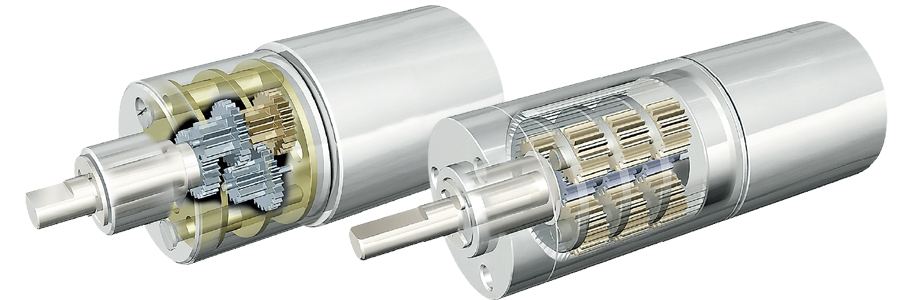
Technical requirements for manufacturing small motors
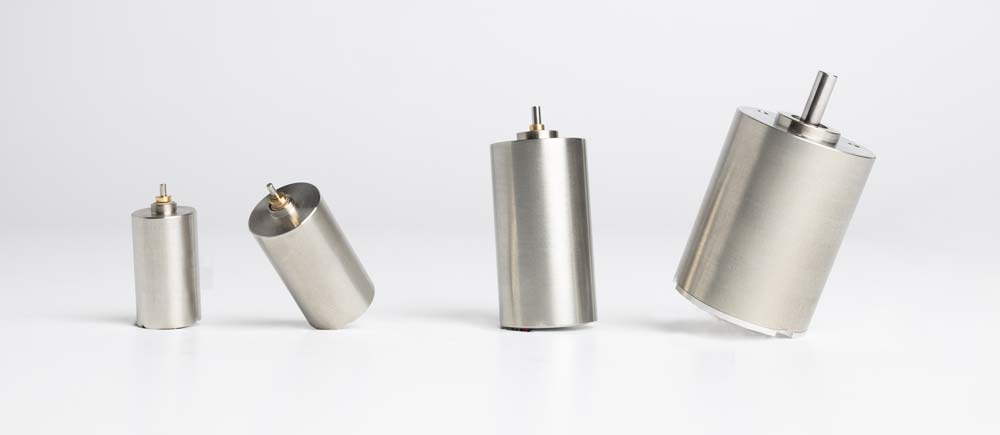
In small motors, the compact internal structure demands that each component meets strict performance and manufacturing requirements. For example, high-performance magnet materials must be precisely processed while maintaining their original properties. Additionally, efficient coils must be manufactured by winding ultra-fine wires at high density. These and other advanced techniques are essential for producing small motors with high torque and low power consumption. Achieving this level of performance requires precision magnet processing, specialized winding methods, and customized winding machines tailored to these requirements.
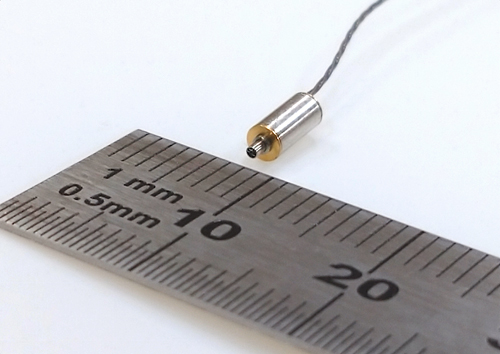
To push the limits of ultra-miniaturization, micromotors with outer diameters of less than 1 mm have been developed. Their small size naturally results in high-speed rotation, making integration with precision reduction mechanisms essential for practical power applications. These reduction mechanisms require fine gears with extremely high precision, measured in just micrometers. Achieving this requires a combination of advanced material development and injection molding technology using precision molds.
Applications of small motors
Medical devices
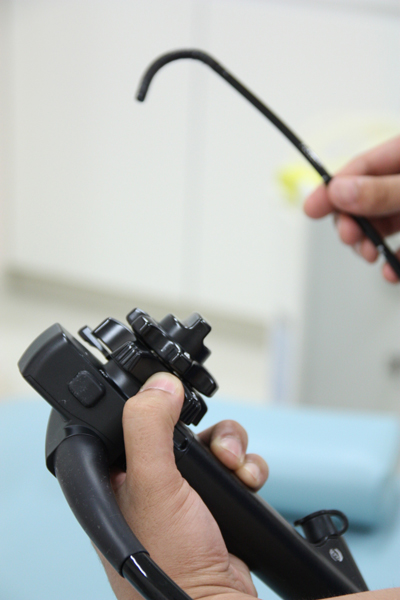
In the medical field, the miniaturization of motors helps reduce the physical burden on patients while enabling more precise treatments. For example, in endoscopic surgery, a small incision is made in the affected area, and micromotors are used to control the movement of the surgical instrument's tip, allowing for precise and minimally invasive procedures.
Micromotors are also used in implantable devices such as artificial hearts and ventricular assist devices. In artificial hearts, they play a crucial role as the power source for the pump that circulates blood.
In everyday medical settings, small motors are used in dental drills. They are also used in mixers for preparing impression materials, which are pressed against teeth to take dental impressions and require thorough and consistent mixing for accurate results.
Top of Form
Industrial equipment
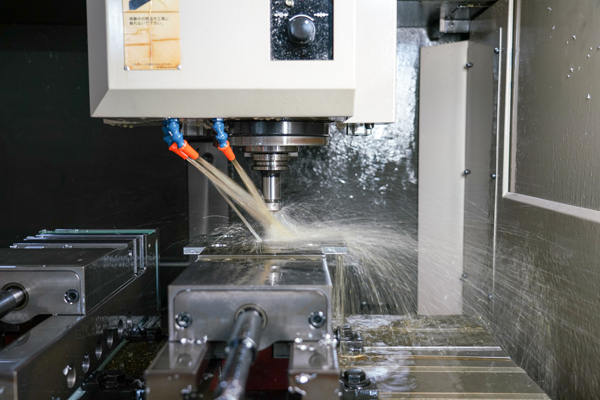

In industrial settings, small motors play a key role in precision-driven processes. They are used in electronic component mounting machines, where they help position, transport, and place electronic components accurately onto circuit boards. Small motors are also integral to machine tools that process metals and resins. By precisely controlling the rotation and movement of cutting tools, they enable the production of complex shapes with high accuracy, much like sculpting intricate designs from raw materials.
Additionally, small motors are used in automated inspection equipment to precisely position and move cameras, sensors, and lighting for inspection of the final quality of manufactured goods. This contributes to the early detection of defects and helps maintain consistent product quality in manufacturing.
Daily life
Small motors are used in many everyday applications, including:
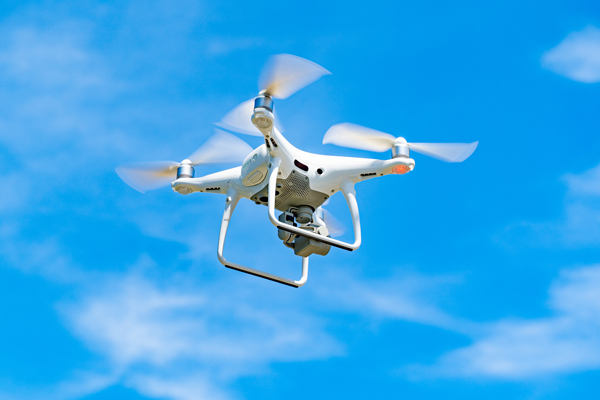

・Smartphone camera modules (image stabilization mechanism)
・Drone propellers
・Haptic vibration motors in wearable devices
・Cordless power tools (drivers, trimmers, etc.)
・Smart home devices (electric curtains, blinds, etc.)
・Cutting-edge medical equipment (surgical support robots, drug administration pumps, etc.)
Summary : Small motors
This article explored the different types of small motors, their operating principles, the advanced technologies behind them, and their wide-ranging applications. From brushed DC motors and coreless motors to brushless DC motors, each type has unique characteristics that make it suited for different applications. Choosing the right motor is crucial for maximizing efficiency and performance.
Small motors play important roles in every aspect of modern life. As technology evolves, they are becoming even smaller, more precise, and more energy-efficient. They power everything from life-saving medical devices and high-precision industrial equipment to everyday conveniences like smart home devices and power tools.
Since developing the world’s smallest DC coreless motor in 1973, Orbray has been at the forefront of innovation, continuously refining and expanding our lineup of high-performance small motors. With exceptional responsiveness and quiet operation, Orbray’s motors are designed to meet the demands of cutting-edge applications.
Follow the link below to explore the full lineup of Orbray’s small and micro motors:
-
What are End Effectors?
-
What is a collaborative robot? An introduction to the functions and performance of collaborative robots

-
Brushless motor vs brushed motor: The features of the Orbray brushless motor.

-
Robotic Hands

-
Servo-drivers: How they are made and how they are used
-
What are grippers? Introduction to industrial processes and common applications. What are grippers?



