What is a collaborative robot? An introduction to the functions and performance of collaborative robots

Warning: Attempt to read property "title" on bool in /home/xb365490/orbray.com/public_html/magazine_en/wp-content/themes/orbray/inc/blogcard.php on line 87
Warning: Attempt to read property "description" on bool in /home/xb365490/orbray.com/public_html/magazine_en/wp-content/themes/orbray/inc/blogcard.php on line 88
At factories such as those that manufacture automobiles and precision equipment, various industrial robots are in operation doing welding, painting, assembly, and other work.
Industrial robots can easily move heavy parts and equipment that people cannot, and can repeat the same operation accurately and at high speed.
They have been used to automate manufacturing lines and have greatly upped production efficiency.
In recent years, however, there has been increasing introduction of collaborative robots which, unlike industrial robots, work together with people.
Collaborative robots are now being used at manufacturing sites where it has previously been difficult to introduce robots, helping to alleviate labor shortages and improve production efficiency.
Table of contents [close]
What is a collaborative robot?
Conventional industrial robots do work with powerful, high-speed operations that far exceed human movements.
Since they are dangerous to be near, they operate in areas isolated by safety fences and on production lines that are exclusively for robots.
They are very useful when manufacturing large quantities of products that are the same size and shape.
On the other hand, they are also very large and require ample space to work, so installation can be a challenge.
By contrast, collaborative robots perform tasks in the same place as and in cooperation with people.
They move similarly to humans, and can respond flexibly to a variety of tasks.
In recent years, labor shortages at production sites have become a serious problem.
At large, mass-production factories, it is possible to compensate by introducing industrial robots for automation.
However, that is not such a viable option for small factories with lower production volumes.
In this case, adding collaborative robots to the manufacturing line as additional workers can help solve labor shortages.
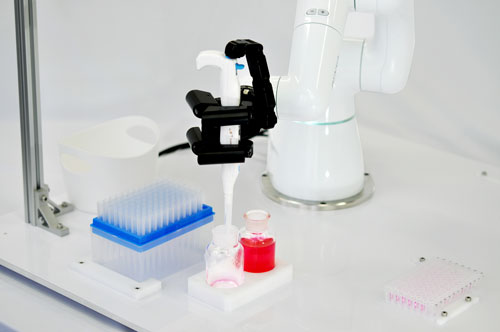
Gripping the test tube by collaborative robot end effector K3HAND
Additionally, user demands are also changing with the times, and the need for high-mix, low-volume and variable lot-size production is on the rise.
These types of production necessitate flexible changing of the production line to increase production efficiency, but large industrial robots cannot handle that easily.
Collaborative robots are compact, lightweight, easy to install, and capable of performing a wide variety of tasks. If there is a change in product type, their operation and installation position can quickly be changed, allowing for flexible manufacturing.
Unlike people, collaborative robots are able to operate continuously with exceptions for maintenance and power loss.
They are also very useful for raising production efficiency; on production lines with multiple shift rotations, they can continue working without needing to change out like a person would.
These benefits make collaborative robots indispensable for supporting future manufacturing sites.
Requirements for collaborative robots: Hands that can perform the same tasks as humans
The performance and function requirements for collaborative robots differ from those of conventional industrial robots.
One such requirement is a hand that can grasp objects delicately like a person.
Collaborative robots do not need to be moved while actively working on a production line, and they can be equipped with tires, etc. for movement, so they do not require legs like a human or animal.
However, hands and arms are necessary to perform the same tasks as people do.
Human hands can grip soft, thin, slippery objects without crushing or breaking them, and even objects with complex shapes can be grasped easily by moving the fingertips to fit the shape.
In order for a collaborative robot to be able to perform human tasks, it needs to be able to freely move its arms and grasp objects in the same way a person does.
There are various types of collaborative robothands, such as hands with many fingers that are articulated and bend intricately, or those that use rubber material to bend flexibly.
Some hands have servo motors that operate precisely, enabling both delicate grip and fine movement.
Different hands can also be changed out according to the work.
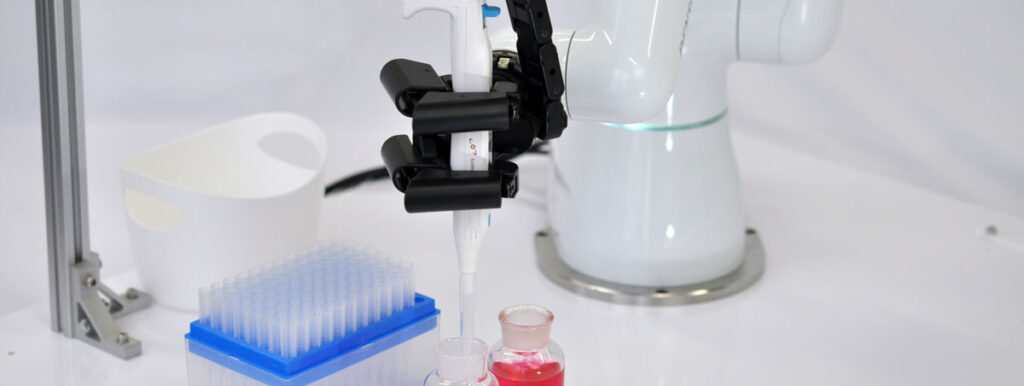
Remote control of collaborative robot end effector K3HAND
In order for the hand to move precisely, it requires control technology, image processing technology for accurately determining the shape and position of the object to be grasped, and sensor technology for adjusting the grip strength.
With well-crafted hands and sophisticated control technology, collaborative robots perform delicate tasks just like people do.
Robot hands are also referred to as end effectors. It is no overstatement to say that a collaborative robot's dexterity relies on the performance of the end effector.
Requirements for collaborative robots: Safety, compactness and light weight
Safety is another important aspect of the performance and functions required of collaborative robots.
Collaborative robots operate in the same environment as people do.
Robots are more powerful and can move at higher speeds than humans, and contact with a person during high-speed operation can result in fatal accidents.
As such, robots must have a function to stop or decelerate when a person comes close to or in contact with them in order to avoid injuries.
Some collaborative robots have an area sensor that detects when a person approaches a certain distance.
This makes it possible to stop or decelerate before contact to avoid accidents.
In addition, some systems have a safety function that automatically stops the robot when a certain amount of force is applied, or absorbs an impact using clutch mechanisms in the unlikely event of a collision with a person.
This way, contact does not lead to a major accident.
Collaborative robots are also required to be compact and lightweight.
They need to be able to be moved easily without taking up an installation place so that their layout can be freely arranged according to the arrangement of people.
If the work place is a food factory or pharmaceutical factory, robots must have a mechanism that prevents things such as oil leaks or falling parts, and they must meet health and sanitary standards.
Collaborative robots need to operate safely according to the actions of the people around them, rather than people having to match the movements of the robot as with industrial robots.
The expanding range of collaborative robot applications
Collaborative robots are being introduced in a variety of industries.
Even in the automotive industry for example, where large industrial robots have traditionally been used, collaborative robots are in operation supporting assembly work done by people.
They have also been introduced on precision equipment production lines to work alongside people, performing various tasks such as moving (kitting) and assembling components, and aligning products.
And on food production lines, they are used for work such as sorting foodstuffs with different shapes into set positions.
Collaborative robots are also used for visual inspection.
Visual inspection requires very delicate observation, and when conducted by a person, fatigue of the inspector can impact the detection accuracy.
This kind of work is well suited to collaborative robots, which can observe products of various shapes from a variety of orientations and angles without tiring.
In addition, collaborative robots are now being utilized not only at manufacturing sites, but also at chemistry and medical sites in work such as bio/physicochemical experiments, drug development tests, and pathology examination.
Collaborative robots with hands capable of delicate movement are ideal for grasping and operating small scientific instruments such as electric pipettes.
They can support the work of medical and research workers 24 hours a day, without rest.
From here on, the scope of applications for collaborative robots will only continue to expand.
Click here for Orbray's K3 Hand, an end effector for collaborative robots
Related article: