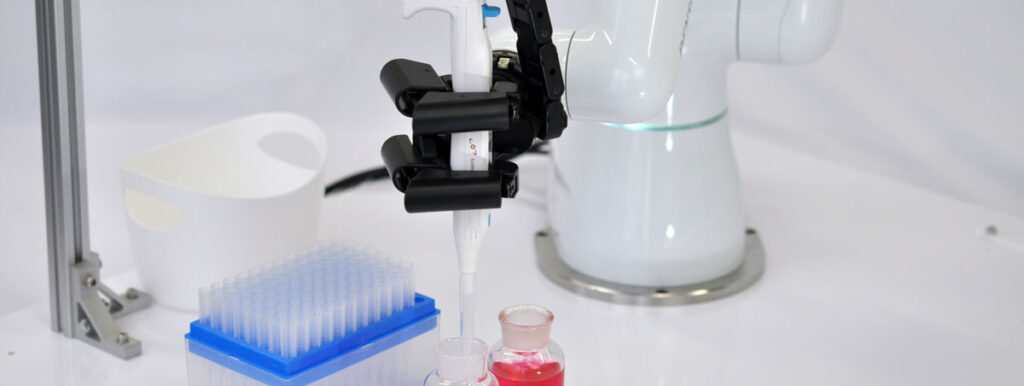
What are grippers? Introduction to industrial processes and common applications. What are grippers?
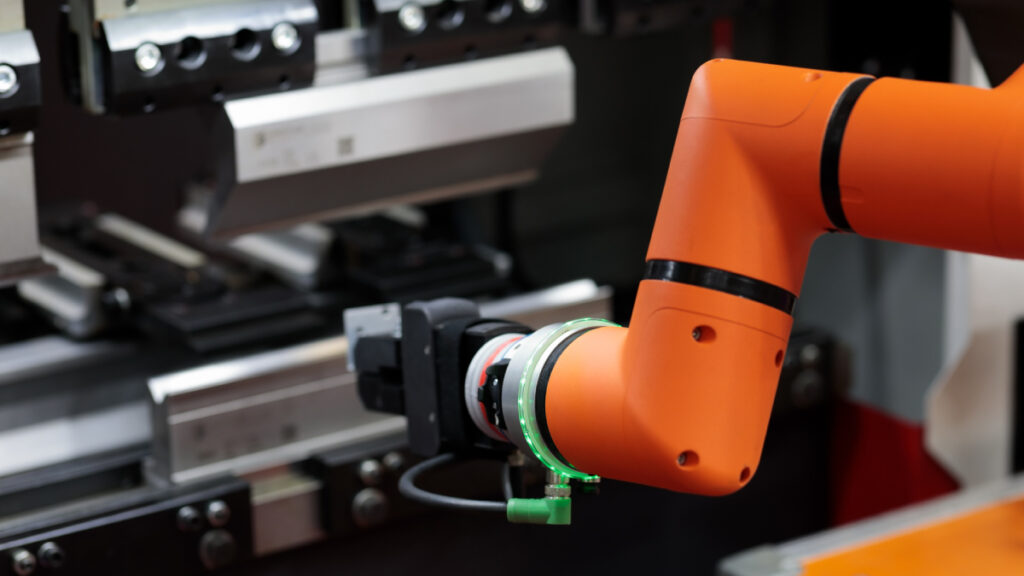

As industrial processes become more automated, the demand for robots continues to grow. The “gripper” is the part of the robot that grabs and holds objects. It plays a significant role in the efficiency and safety of manufacturing processes.
However, there are many cases in which the importance of proper gripper selection is underappreciated, resulting in less than optimal results.
This article will take a closer look at the types of grippers, pros and cons of each, and example applications of these important pieces of robotics equipment.
Table of contents [close]
What are grippers?
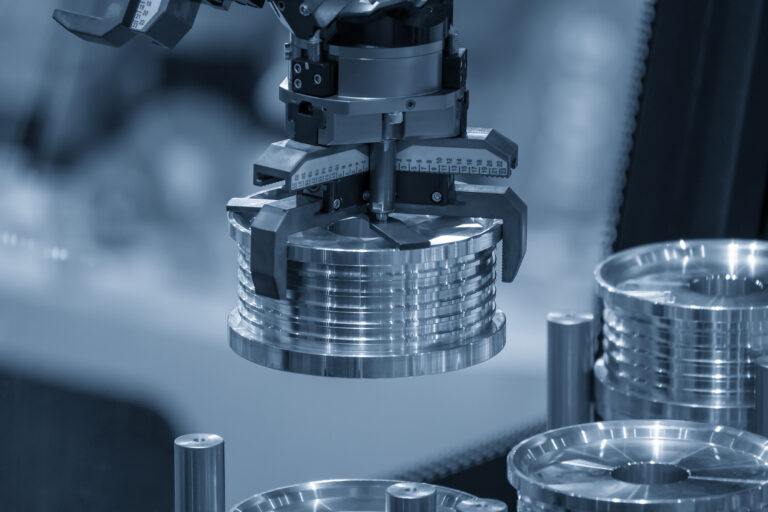

Grippers are devices that grip and hold objects and are essential to robotics. They are used, for example, in production lines and logistics centers where robots grab parts or products and move them to where they are needed.
Grippers act like the “hands” of robots. They come in many different sizes and with many different functions depending upon the objects they handle and the work that needs to be done. Grippers are commonly categorized as below.
- Precision control grippers for gripping and handling very small electronics components.
- Strong, industrial grippers for picking up and moving very big and heavy objects.
Grippers can also function as end effectors. End effectors are attached to the ends of robot arms and have built-in equipment that allows them to do work directly. They are the interface with which the robot interacts with the work piece and greatly affect the productivity of the robot.
Find out more about Orbray’s end effectors, here:
Industries that use grippers

In addition to production lines, grippers are used in many other industries. This section will describe some industries in which grippers are used, how they are used, and benefits.
Industries and applications
Grippers are widely used in many industries due to their versatility and high functionality. They are beneficial in the following ways.
- Speed
Precise work that is time-consuming can be automated with robots. This time-saving automation speeds up production and increases market competitiveness.
- Quality assurance
Repetitive work that is straining to workers can be entrusted to robots. Inconsistencies between workers or reduced attention due to fatigue can be eliminated, helping to ensure consistent quality of products.
Plastics and polymer production
Robots with grippers are used for processes such as injection molding and blow molding, where workpieces are put into and taken out of machines repeatedly, and for processing work using 3D printers. Human labor no longer needs to be used for menial tasks, which can lead to cost reduction and productivity improvement.
Chances for human error can also be reduced.
Food industry
Maintaining a hygienic environment is essential in the food industry. Robots with grippers can handle food faster and more hygienically than human hands. Grippers are also used in robots that perform secondary processes such as wrapping and packing. They also find work in greenhouses, cold rooms, and quality inspection steps.
Medicine and research
In the fields of medicine and research, liquids and chemicals must be measured and mixed in very precise volumes using flasks and other measuring methods. Consistency is essential to ensure that results are accurate. On top of that, some of these chemicals can be harmful to human health. Robots with grippers can be used to safely and accurately perform work that was previously difficult and dangerous to do manually.
Benefits of using grippers
There are three major benefits to using grippers. The first is reduction of labor costs. Work done by human labor can be automated by robots equipped with the appropriate gripper, greatly reducing labor costs.
The second is improvement of production efficiency. Robots don’t need to take breaks or have limits on the number of hours they can work in a day. Mass production of products can be done efficiently 24 hours a day by robots, improving resource use efficiency.
The third benefit is the ability to do work that humans cannot. Grippers can be used to lift very heavy objects. They can also work in very hot or cold environments. Likewise, they can perform high-precision work repeatedly, a feat that is difficult for most humans to do sustainably. Errors can be all but eliminated with the proper maintenance, and high-quality production can be achieved around the clock.
Pros and cons of different types of grippers

Grippers can be largely categorized as pneumatic (air pressure) and electric grippers. This section compares the pros and cons of the two types, including weight, accessories, and other characteristics.
Pros and cons of pneumatic grippers
Pneumatic grippers open and close by air pressure being sent to the fingers of the grippers. Solenoid valves can be used to send high-pressure air available in the factory to the grippers to open and close them.
The grippers can be operated with just the opening and closing of valves, and simple relays can be used to control them. They are also lightweight. This allows the robots arms to which they are attached to carry heavier loads.
In addition, pneumatic grippers have a relatively simple construction, leading to reduced initial investments. This makes them easy to implement in new operations and processes.
However, pneumatic grippers are not suitable for holding objects for a long time. It is also difficult for them to grip objects of different sizes. The holding power of pneumatic grippers is directly correlated to the air pressure being applied to them. Pressure must be maintained for them to keep a hold of an object. Operations in which grip strength must be carefully controlled requires careful control of air pressure, which is difficult in many circumstances.
Pros and cons of electric grippers
Electric grippers are operated by electric power. They contain motors and articulation gears that can be controlled to determine the speed and strength of the gripper movements. Micro motors are commonly used, as they can fit inside the gripper structure.
With electric grippers, many different working and gripping positions can be set in a row. They can also handle objects of different sizes or those facing different directions. A single gripper platform can be used to perform many different operations on different work pieces. These are major advantages of electric grippers. Since the grippers are operated by motors, many different actions can be programmed. This is advantageous when high precision is required.
However, when compared to pneumatic grippers of similar size, electric grippers tend to be less powerful. This is one clear disadvantage to be aware of when considering the use of grippers in production.
In addition, when installing electric grippers, PLC controllers are needed, requiring a certain level of cost and expertise to deploy electric grippers in production.
Important points when selecting a gripper

When selecting a gripper, the characteristics of the work piece and the work required must be considered carefully. This section explores the functional characteristics such as the shape, strength, and rigidity of grippers, as well as passive characteristics like dustproof and waterproof performance.
Gripper shape
There are many different shapes and arrangements of the fingers of grippers. Most grippers have between two to five fingers. Grippers used for manufacturing processes commonly have two or three.
Two-finger grippers are effective for holding most objects. However, for round objects or those with irregular shapes, three-finger grippers are better.
Opening/closing movement can be categorized as either parallel open/close or joint open/close. In parallel grippers, the gripping surfaces slide to open and close. This allows them to grip with high precision and strength. The fingers of a joint gripper move on a fulcrum. This allows the opening to become larger.
Grip Strength
The hardness and weight of the work piece, as well as the work environment, need to be considered when selecting a gripper with the correct grip strength. High grip strength is required when handling very heavy objects or if there are lots of vibrations in the work area.
However, the work piece can be damaged if the grip strength is too strong. When working with soft, delicate, or precision products, the stress tolerances of the products must be checked carefully and taken into consideration.
In addition, the desired behaviors after gripping, such as movement speed and position must also be considered.
Rigidity
Rigidity is the resistance of an object to outside forces. Rigidity relates to the durability and stability of the fingers of grippers.
Rigid grippers have less rattling between the gripper and fingers. This contributes to very stable operations, especially suited for precision gripping work. Service life is also high, so frequency of maintenance can be reduced.
Dust and water resistance
In certain environments, dust and water resistance become important. For example, in environments where dust is generated or the gripper may be splashed with water, the life and stable performance of the gripper can be maintained if it is a dustproof or waterproof gripper.
Gripper summary
Grippers are essential devices that allow robots to grab and hold objects. There are many kinds of grippers depending on the use, environment, and the characteristics of the object to be gripped. By selecting and using the appropriate gripper, work can be automated and made safer and more efficient.
In addition, the performance of electric grippers is highly influenced by the motors used to drive them. In particular, Orbray's micro motors feature precision movement, low vibration, and high responsiveness, and are expected to play an active role as the cornerstone of grippers that perform precision work.
Find out more about Orbray’s micro motor and small motor here: