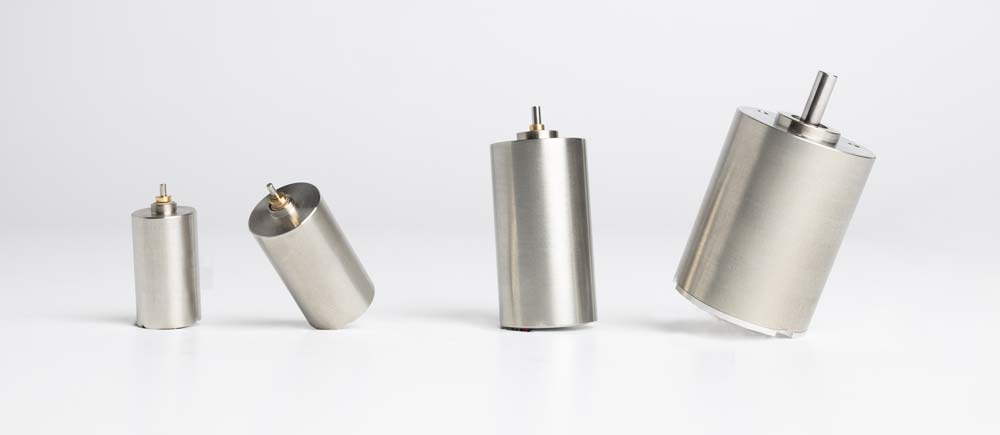
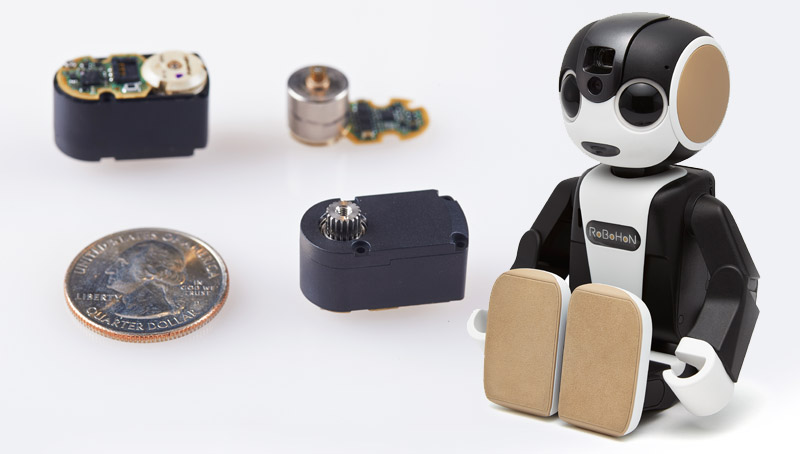
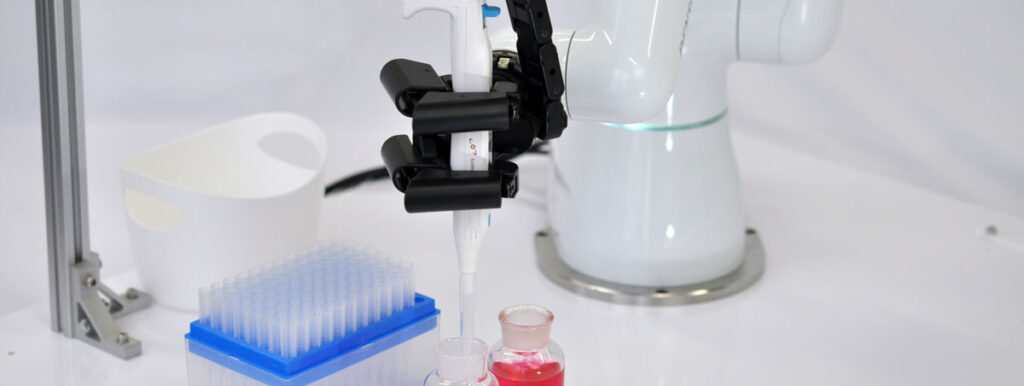
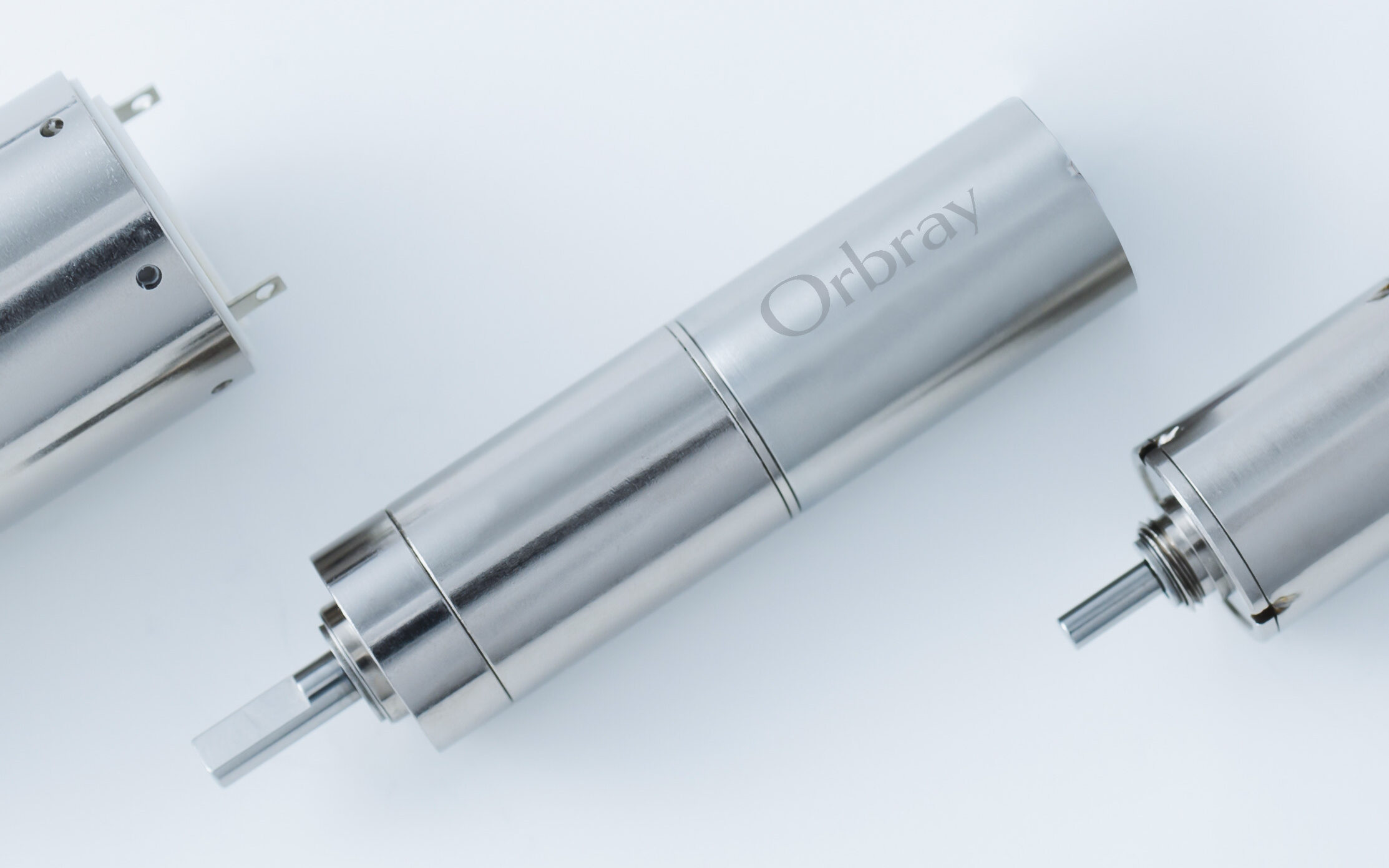
What is a Geared Motor?

An electric motor and gearhead combination is called a geared motor. A gearhead usually aims to boost the motor's output torque and restrict the rotational speed of the motor's shaft. Including an appropriately sized and constructed gearhead makes it feasible to achieve the desired output speed and torque.
The electricity used by the geared motor may be either DC (direct current) or AC (alternating current), depending on the kind of electric motor attached to the gearhead.
In this blog, we will discuss the types, benefits, and working geared motors to help you understand their usage.
Table of contents [close]
Types of Geared Motor?

In the field of mechanics, geared motors have always been regarded as vital components, and their success comes from their practicality. Let's take a look at each type of geared motor.
Spur Geared Motor
Spur gears generally have teeth arranged radially parallel to the axis. A small gear on the input side meshes with a large gear on the output side at one point per stage.
This meshing structure reduces revolutions per minute (RPM), converting into torque.
These motors typically produce low mechanical noise while offering higher power than motor only and efficiency.
These are composed of various materials such as steel, brass, and so on.
Spur-geared motors have vast applications in different industries ranging from automotive systems to conveyor systems. Some of its key applications include powering conveyor belts, controlling the movements of robotic arms, and providing mechanical motions for vehicle functions such as seat adjustments, power windows, etc.
Planetary Geared Motor
As the name indicates, these geared motors work the same as planets rotating around the sun. There's a sun gear at the center and planet gears rotating around it (typically on a carrier). There's another gear with inward-facing teeth known as ring gears that hold planet gears around the center to orbit about the sun gear.
These are designed to provide higher torque and power in a comparable volume compared to a spur gearhead. This kind of gearhead has the benefit of having less backlash.
The number of teeth and size of planetary gears are modified to alter the speed and torque of output. Spur gears mesh at one location per combination, whereas planetary gears mesh at multiple locations to disperse force, improving durability and service life.
These also have higher load capacity.
Advantages of Geared Motor
Geared motor consist of a Gearhead that is connected to the motor directly. This means that because the motor pinion now meshes with the input gear of the gearhead, so there's no need for a motor adapter or connection.
Eliminating these extra parts makes the solution lighter, more efficient, and has fewer wear parts, which means you and your team will need less service.
There are several more benefits of a geared motor. Let's review their main advantages:
Cost Effective
Profits are usually immediate because many gear motors are low-maintenance and affordable to install; it makes system repairs easier.
Torque Multiplication
This is beneficial for applications requiring higher torques. The size and specifications of motors vary based on their use. Large sized motors are used in elevators and conveyors. On the other hand, medical and optical equipment require smaller and more precise motors due to the nature of their use.
Speed Reduction
The gears installed in a geared motor are sometimes called reducers because they increase the output torque and reduce the output speed at the same time. This speed reduction enhances system performance since many motors themselves are inefficient at low rpm in general.
Space Efficiency
Geared motors are typically considered a space-efficient option. Even though it is smaller in size, these motors still deliver the required torque. This is especially helpful in scenarios where space constraint is a concern.
Uses of Geared Motor
Geared motors are used for applications requiring a high output torque and a low output shaft rotation speed, particularly those with limited space and power. This covers a broad spectrum of typical equipment uses in several sectors.
Robotics
Geared motors are widely used in the robotics industry, especially for actuating different joints, e.g., arms and limbs. In revolutionary robot hands, these motors allow freedom movement with the actuator mechanism. Motors also provide high torque, especially when these robot hands are required to lift or support heavy loads. Their high durability counters the wear and tear caused by repeated movements, ensuring a longer life span for the machines.
These motors are also key components of multi-axis robots and its end effector, allowing them to move in a specific direction with a controlled speed.
Semiconductor Manufacturing Equipment
Geared motors are also widely employed in semiconductor manufacturing facilities. Geared motor including high precision-processing gear allows for controlled movement and accurate positioning in handling and transporting different components.
These are also important in mounter head devices that are needed at the mount stage of semiconductors for arranging different parts. As parts become smaller, the motors installed in them are also tends to be smaller.
Medical Equipment
Due to their reliability, hundreds of medical equipment like endoscopes and injection pumps use geared motors.
In addition, medical equipment requires quietness, so it is necessary to prepare gears that are specialized for quietness, such as those made of resin.
The Bottom Line
Different kinds of gearheads are needed for different purposes. To ensure that equipment operates smoothly and for an extended period, Orbray geared motors are constructed from various factors selected for their intended purpose. We provide smaller diameter motors starting from φ4.
From medical equipment to security cameras, drones to dust masks, Orbray provides components based on your particular requirements for every use.
Contact our professionals at Orbray if you need clarification on the appropriate geared motor for your specific need!