Robotic Hands
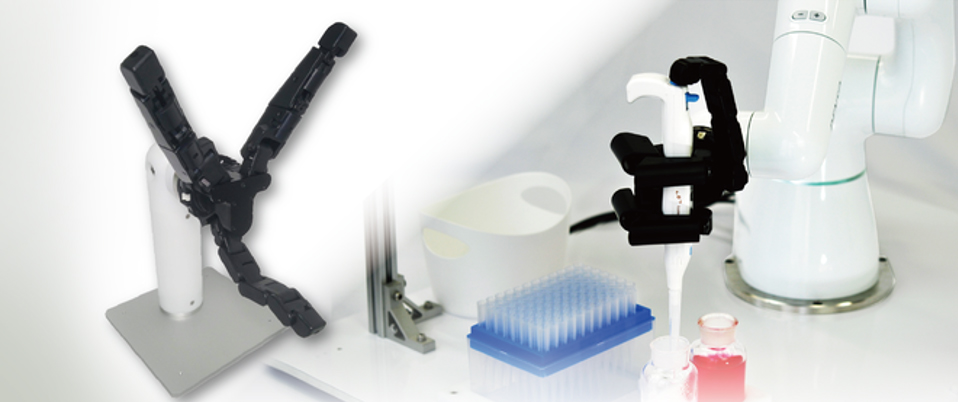

Robotic hands are one type of end effector for robotic arms. Attached to the ends of robotic arms, they are able to perform tasks similar to human hands. Robotic arms are used in a variety of fields and applications, such as processing, moving, and assembling parts in factories; transporting goods in warehouses; dispensing chemicals in drug development; and many other fields.
Table of contents [close]
Types and features of robotic hands
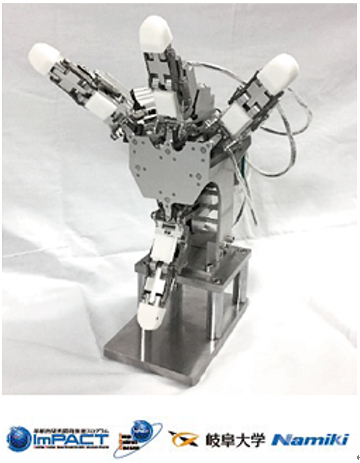
Robotic hands are attached to the ends of robotic arms and perform various tasks like a human hand.
For example, some robotic hands have two or three fingers. These hands are able to grasp objects, just like the human hand. Robotic hands with multiple articulated joints are capable of even more detailed movements and can pick up complex objects. Some robotic hands are fitted with soft, rubber fingers. Such hands can wrap themselves around the contours of delicate objects and gently pick them up without damaging them. Other robotic hands are fitted with suction cups or magnets, allowing them to securely handle smooth or metallic objects. A wide variety of robotic hands have been developed to meet the specific needs of various applications.
Uses of robotic hands
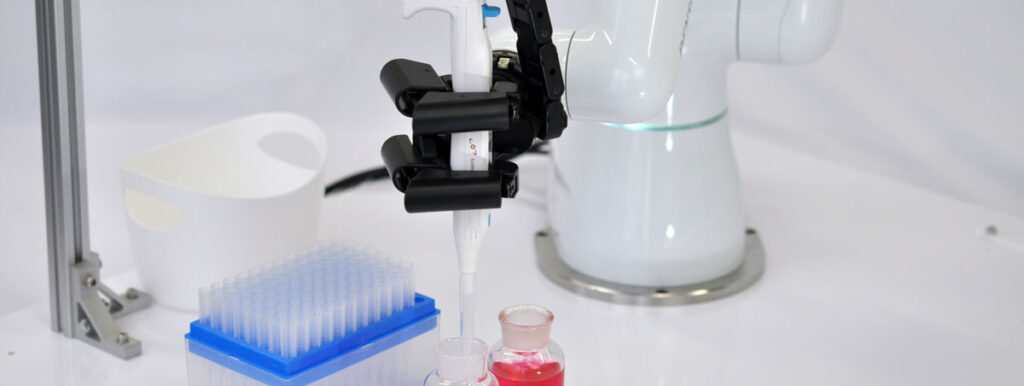
Robotic hands can perform a wide variety of tasks, such as gripping, moving, and rotating objects, and some can even operate switches as they hold them. For example, robotic hands attached to the ends of SCARA (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm) robots in factories can pick up small parts with their fingers and move them into place for assembly. Robotic hands used in medical and chemical inspection processes can hold multiple pipettes in the same way as human hands, and accurately measure out and dispense specified chemicals into a large number of test tubes. In the food processing industry, robotic hands are used to grab and move food items without crushing them. Collaborative robots, or cobots, have gain popularity in recent years, and have been installed in many factories. Cobots work alongside human workers by grabbing tools and manipulating them together with their human counterparts.
Robotic hands are especially useful for performing simple, repetitive, and continuous tasks in harsh environments accurately, quickly, and safely, for extended periods of time. They are also used in manufacturing sites that require highly hygienic conditions, such as food processing facilities, so that manufacturing can be done without human intervention and quality can be maintained.
Robotic hands can contribute greatly to improved process efficiency and quality, and reduced labor costs.
K³ Hand dispensing System
Power sources and applications of robotic hands
Depending on the application, infrastructure, and surrounding environment, robotic hands can be driven pneumatically (compressed air or vacuum), hydraulically, or electrically. Pneumatic hands are used to suction and transport objects, or to pinch and pick up objects with a specified amount of force. Hydraulic hands are most often used for gripping and transporting heavy objects. Electric hands with small motors are common in applications that require delicate movements similar to human hands, such as grasping and moving small parts with high precision, and handling soft or delicate objects. As micro-motors are better at controlling the amount of movement and force more precisely than pneumatics or hydraulics, they are more suitable for robotic hands that perform delicate work.

Micro-motors for efficient robotic hand operation
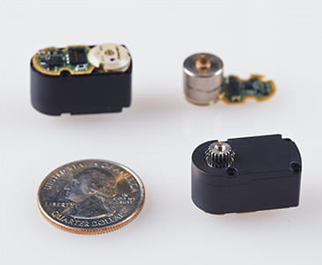
Robotic hands that are made to mimic the human hand require multiple finger joints, and each joint requires a motor to move it. Furthermore, to grasp and manipulate objects that are made for human hands, the robotic hand must be a similar size. This means that the motors inside the human-sized hand must be quite small. These small motors must also be capable of precise movement. In addition to the drive mechanism, the motor must also include a clutch mechanism so that force can be released if the fingers experience sudden, unexpected loads.
Conventional robotic hands require continuous supply of high power to sustain their grip on an object. This means that even momentary power interruption could loosen the grip and cause the object to fall. If the grip can be maintained by locking the fingers in place, the object can be held safely even if the power suddenly fails. Such a locking system can reduce power consumption and heat generation, allowing robotic hands to operate more efficiently and reliably.
Video of clutch mechanism (Torque limiter)
-
The World’s Smallest Hollow Shaft Motor
-
What is a Geared Motor?

-
What are grippers? Introduction to industrial processes and common applications. What are grippers?

-
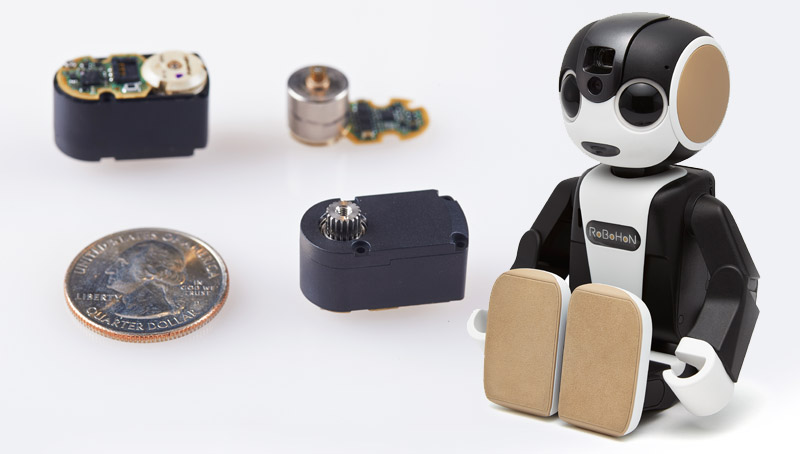
Small Servo Motor for Robot Joints

-
Brushless motor vs brushed motor: The features of the Orbray brushless motor.

-
What are End Effectors?