What are Diamonds?

When speaking about gems or jewels, most people think of diamonds. The word diamond comes from an ancient Greek word adamant, which means “solid and unrivaled.” This is also where our company name comes from.
Diamonds are made of carbon. In this sense, diamonds are the same as common pencil lead. However, the carbon atoms are arranged in different patterns and give the two substances very different characteristics. Everyone knows that diamonds are very hard and give off an almost mystical shine. Impurities are one factor that can cause diamonds to have color. A very pure diamond with no impurities is completely colorless and transparent. Colored diamonds also exist. Diamonds are categorized into the four types shown in Table-1, depending on the amount and distribution of the impurities. This is the scientific classification of diamonds, and differs from the 4C(*1) categorization system used to classify ornamental diamonds and assess their commercial value.
| I型 | Ⅱ型 | |||
| Ia | Ib | Ⅱa | Ⅱb | |
| Nitrogen Content [wtppm] | 3,000 (clustered) | >500 (diffuse) | <20 (displaced) | ~0 |
| Boron Content[wtppm] | 0 | 0 | 0 | ~20 |
| Color | colorless or yellow | yellow or brown | colorless | blue |
| Natural occurrence[%] | ~98 | ~0.1 | 1~2 | ~0 |
Naturally occurring blue and pink diamonds are very rare and are extremely valuable. Recent technological innovations have resulted in the development of methods for producing colorless or yellow diamonds, and methods for adding color to colorless diamonds through irradiation or heat treatment.
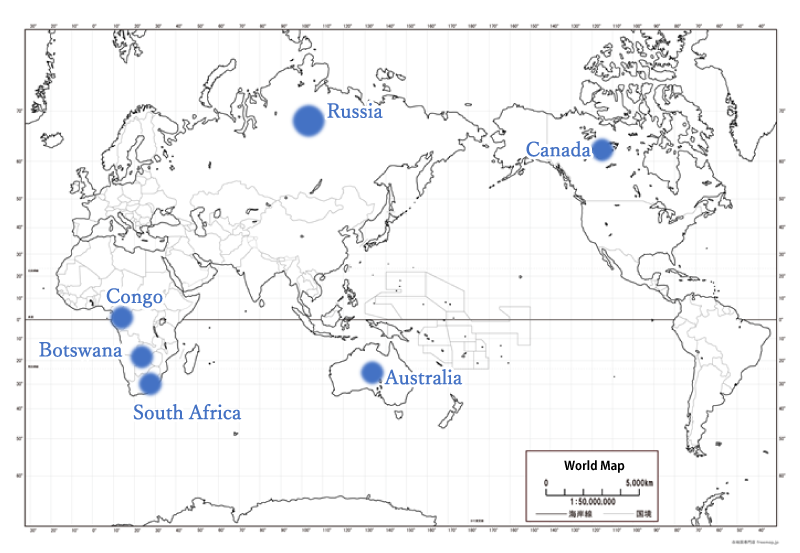
The major global producers of diamonds are Russia, Botswana, The Congo, Australia, and Canada. These five countries produced 80% of the world’s supply in 2018. Until recently, it was thought that diamonds could only be mined where ancient geological structures were still intact, and could not be found in Japan where geological features are relatively new. However, some tiny diamonds about 1 micron in diameter were found in Ehime prefecture in 2007, and became a very hot topic.
In the next article, we will discuss what people have been dreaming of for millennia: Technology for producing artificial diamonds.
Explanation of terms: *1: Diamond quality assessment method adopted by 4C and Gemological Institute of America (GIA). Diamonds are evaluated across four qualities: Cut, Clarity, Carat, and Color.
-
What is an audio accessory? An overview and detailed explanation of products
-
What is an audio accessory? An overview and detailed explanation of products [Part 2]

-
History of Orbray crystal glass [Story of Watch 3]

-
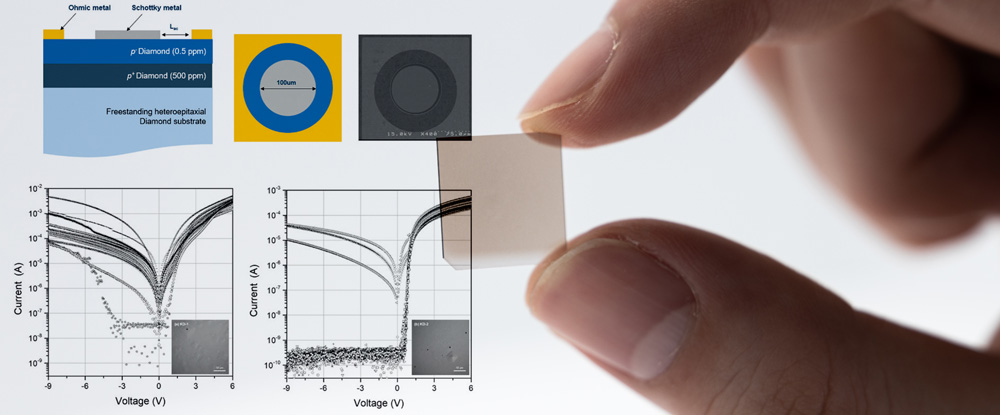
We were featured on the cover of the journal Diamond and Related Materials.
-
First round of Space Delivery Project “RETURN to EARTH” The ceremony celebrating the return of the payload items was held

-
Watch Parts: Beautiful work of craftsmanship -the world's first artificial diamond parts-



