Brushless motor vs brushed motor: The features of the Orbray brushless motor.

What is the difference between a brushless motor and a brushed motor?
Explaining the features of the Orbray brushless motors.
Table of contents [close]
What is a brushless motor?
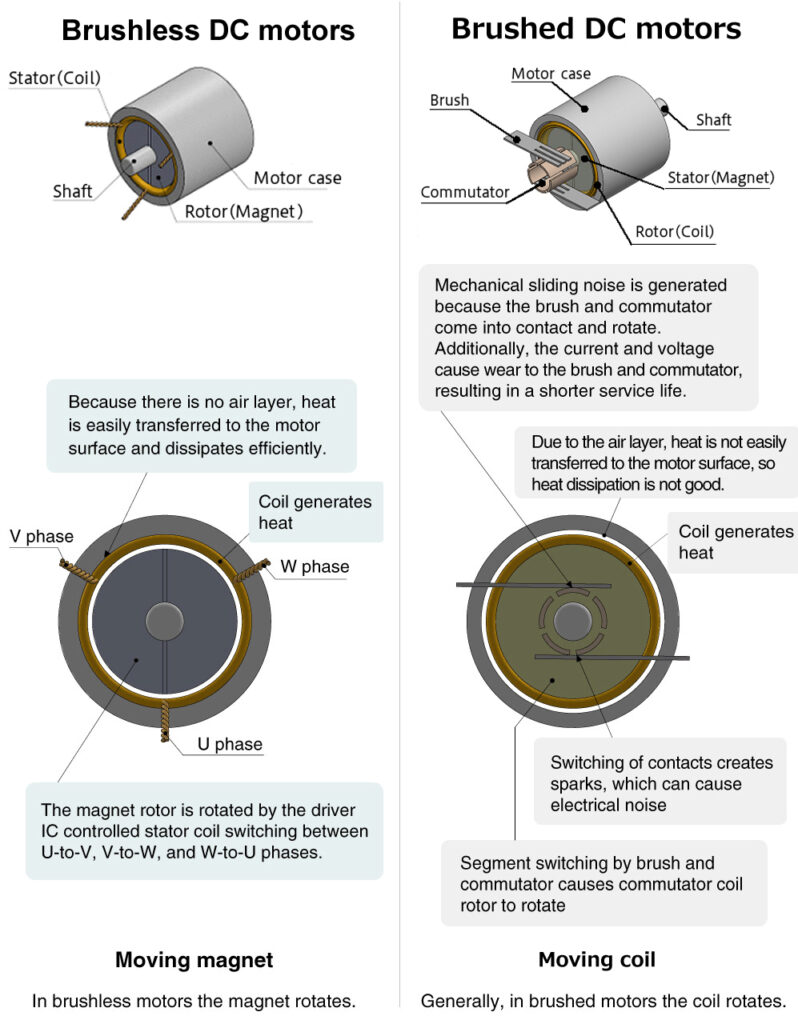
A brushless motor is a motor in which the mechanical parts that come into contact with each other, such as commutators and brushes, have been removed.
In conventional motors, a commutator and brushes are used to mechanically reverse the positive and negative electrical charges that drive the motor, but the friction of the brushes against the commutator causes those parts to wear out, as well as other problems, resulting in a short service life for the motor.
With the widespread use of semiconductors, electronic circuits are able to produce the magnetic fields that cause the motor to rotate, thereby eliminating the need for commutators and brushes.
The resulting brushless motor has a longer life than motors using mechanical commutators.
Find more information about our brushless motor here:
Differences between a brushless motor and a brushed motor
1: Heat dissipation
In a coreless motor with a brush, there is a gap (layer of air) between the rotating coil and the motor housing, so heat generated by energization is not easily transferred to the outside.
In contrast, in a brushless motor, the magnet rotates and the coil is fixed in close contact with the outer core, so the heat from the coil is easily transferred to the motor surface, resulting in high-efficiency heat dissipation.
If the temperature inside the motor rises too much, the magnet may be demagnetized and performance may deteriorate.
For this reason, brushless systems with high heat dissipation are more advantageous for higher power uses.
2: Large current/high power
In a brushed motor, the commutator on the rotor side and the brush on the stator side slide while energizing. If a large current is applied, the electrical contact may melt and fail, so there are limitations on power input.
In a brushless motor, the driver circuit controls the externally-energized coil, so there is no contact point, and this along with high heat dissipation means a large current can be applied to the motor.
3: Mechanical noise
Brushed motor
A brushed motor generates a mechanical sliding noise due to the contacts rubbing against each other. In addition, when the contacts switch with rotation, sparks are generated at the contacts, which causes electrical noise.
Brushless motor
A brushless system has no contacts and therefore no noise source.
A brushless motor has better heat dissipation, higher maximum rotation speed, longer life, and less noise than a brushed motor. However, unlike a brushed motor, which can be operated simply by connecting it to a power source, a brushless motor needs a control circuit for operation. Selection of the appropriate control circuit depends on whether the motor has a sensor that detects the rotor position.
Brushless servo driver (Reference): Motor Drive Circuit SSD06-R5A / SHSD24-01A
Characteristics of the Orbray brushed motor
Comparing the generally slotted armature type (with iron core) brush motors with Orbray's coreless brush motors, our brush motors are characterized by smaller coil leakage inductance and better commutation conditions because the armature winding is not in a slot.
Since there is little variation in magnetic resistance, cogging (torque pulsation caused by the iron core) is eliminated, which means the motor produces very little electrical noise.
Characteristics of the Orbray brushless motor
A non-contact motor allows extremely high power and a long service life, ensuring high reliability.
Orbray's brushless motor has a slotless structure, without slots in the stator.
Such slots (gaps in the magnetic core) can cause cogging (rotation pulsation) because the magnet attracts the convex portion between the slots.
This cogging produces vibration and noise, and affects rotational accuracy and smoothness.
Orbray's brushless motor has cup-like coils installed in the core, and the rotor's magnet is placed inside.
As a result, the coil and the magnet are subjected to uniform magnetic attraction regardless of the position of the rotor, thus enabling smooth rotation without cogging.
The Orbray micro brushless motor is especially suitable for applications such as robots and medical equipment that are particularly sensitive to factors such as torque and require a long service life.
Product lineup
At Orbray, we utilize the technology we have cultivated through the development of the world's smallest motors, and we offer a brushless motor with a wide product lineup starting from φ4mm.
The compactness, torque, service life, quietness, and low level of vibration of our brushless motor offer solutions for applications that require high performance in a limited space, such as portable equipment, robots that need quick response time and delicate movements to effectively communicate, special astronomical telescopes that require actuators to be placed in a narrow pitch, and joint actuation in robotic hands for precise movements.
Extending the life of a brushless motor
The B4S series motor in our brushless motor lineup is a high-torque motor employing a 4-pole magnet.
By changing the magnet from the usual 2 poles to 4, the effective magnetic flux area is increased, improving the torque constant and reducing the current consumption.
The improved mechanical time constant further increases the ease of starting the motor and adjusting its speed.
The B4S series also uses ball bearings as standard, and high torque is supported by the efficacy and reliability of the design.
Comparison of Brushed and Brushless Motors by Application
【Legend】
◎:Optimal (delivers the best performance)
○:Suitable
△:Usable but not optimal
Medical devices
| Application | Brushed Motor | Brushless Motor | Key Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anesthetic devices | ○ | ◎ | Quiet and consistent operation are critical. Brushless motors provide consistent, silent operation with no cogging. |
| Endoscopes | ○ | ◎ | Smooth and precise movements free of vibrations are required. Quality and safety are critical. |
| Drug delivery pumps | ◎ | ○ | Lightweight, compact size, and low power consumption are critical, especially for battery powered pumps. Precise control based on feedback is also important. |
| Dental handpieces | ○ | ◎ | High rotational speed, low vibration, and durability directly impact patient comfort and precision of dental work. |
| Medical pumps | ◎ | ○ | Consistent flow rate, low noise, and high reliability are essential for life-sustaining devices such as dialysis systems. |
Precision instruments and measuring devices
| Application | Brushed Motor | Brushless Motor | Key Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Telescopes | △ | ◎ | Precise movement, compact size, and positioning accuracy are essential for astronomical observations. |
| Measuring devices | ◎ | ○ | Consistent operation at set speed and smooth movement are critical. High responsiveness is required. |
| Microscope stages | △ | ◎ | Precise positioning, suppression of vibrations, and stability at low speeds are essential for accuracy in research and survey settings. |
| Analyzers | ○ | ◎ | Precise speed control, long-term stability, and low heat generation are required to ensure repeatability. |
| Optical focus mechanisms | ○ | ◎ | Precise positioning and minimal backlash are required. |
Semiconductor manufacturing devices
| Application | Brushed Motor | Brushless Motor | Key Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mounter heads | △ | ◎ | Small size, precise positioning, and compatibility with hollow shafts are required. Semiconductor manufacturing requires precise movements done very quickly. |
| Tape feeders | ◎ | ○ | Thin design and precise positioning are required. Demand for flat motors is increasing. |
| Wafer delivery robots | △ | ◎ | Precise positioning, compliance with cleanroom requirements, and minimal particle generation are required. Direct link to manufacturing yield. |
| Inspection equipment | ○ | ◎ | High-speed, high-accuracy operation with long-term stability is critical for quality assurance. |
Robotics
| Application | Brushed Motor | Brushless Motor | Key Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Robotic hands | △ | ◎ | Multiple degrees of freedom, compact size, high power output, and passive holding ability are important features. Compact size is especially important as the drive mechanism must fit inside the limited space available in moving joints. |
| Communication robots | △ | ◎ | Long operation time, high torque, and quiet operation are essential. Quietness is especially important because these robots are designed to communicate with people. |
| End effectors | △ | ◎ | Compact size, high power output, high efficiency, and heat suppression are critical. Efficiency is particularly important to address heat buildup during gripping tasks. |
| Collaborative robot joints | △ | ◎ | High torque density, precise control, and safety are essential. These factors ensure the flexibility and safety required for collaborative work with humans. |
Video and broadcasting equipment
| Application | Brushed Motor | Brushless Motor | Key Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone gimbals | △ | ◎ | Light weight and responsive control are essential. Instantaneous reaction to camera motion and multi-axis stabilization are required. |
| Broadcast camera lenses | ◎ | ○ | High responsiveness, quiet operation, and low-voltage operation are desired. Operation must be quiet to avoid motor noise being captured in the recording. |
| Camera autofocus | ◎ | ○ | Fast response, low power consumption, and quiet operation are essential as these factors directly affect the quality of the photographing experience. |
| Professional projectors | ○ | ◎ | Long service life, silent operation, and consistent performance are required. Must support long-term use. |
Security and industrial equipment
| Application | Brushed Motor | Brushless Motor | Key Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Electronic locks | ◎ | △ | Good responsiveness, tolerance to high and low temperatures, and long operational life are critical. Must be durable across high number of lock/unlock cycles. |
| Security cameras | ◎ | △ | Long life, tolerance to low temperatures and good responsiveness are critical. Must be highly reliable as operation is 24/7. |
| Pan/tilt mechanisms for security cameras | ○ | ◎ | Precise positioning, quiet operation, and weather resistance are required—especially for outdoor installations. |
Office and household devices
| Application | Brushed Motor | Brushless Motor | Key Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Air purifier fans | ○ | ◎ | Quiet, efficient, and long-term operation. Must support 24/7 operation. |
Hobby and leisure
| Application | Brushed Motor | Brushless Motor | Key Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Radio control (RC) | ○ | ◎ | Good responsiveness and high torque are desired. Ultra-fast response (under 15 ms) is often required. |
| Electric fishing reels | ○ | ◎ | High torque, water resistance, and battery efficiency are critical for extended outdoor use. |
Personal care and specialty devices
| Application | Brushed Motor | Brushless Motor | Key Selection Criteria |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dust mask fans | ◎ | △ | Good responsiveness, low power consumption, and low-profile design are critical. Operation must synchronize with the user’s breathing pattern. |
| Tattoo machines | ◎ | ○ | High speed rotation and low vibration are critical. Vibration suppression is essential to reduce operator fatigue. |
Important criteria when selecting a motor
Applications where brushed motors are optimal
- When cost effectiveness is important: Typically more affordable than brushless motors.
- When control requirements are simple: Do not require complex control circuits.
- In battery powered portable devices: Power-efficient due to lightweight rotating coil (rotor).
- In high and low temperatures: Design can be optimized for extreme temperatures.
- Frequent start/stop cycles: Excellent responsiveness for rapid operation.
Applications where brushless motors are optimal
- Long-life applications: No brush wear enables extended lifespan.
- When quiet operation required: Minimal motor noise ensures low sound levels.
- When precise positioning is required: Smooth, stable operation with minimal deviation over time.
- When high efficiency and low heat generation are required: Excellent energy performance with reduced thermal output.
- High-speed operation: Maintains consistent performance at high RPMs.
Key considerations for motor selection:
- Size and weight: Choose the right dimensions for your design requirements.
- Torque and efficiency: Balance performance with energy usage.
- Control complexity: Match the required precision with system complexity.
- Operating environment: Consider temperature, humidity, vibration, and other environmental conditions.
- Total cost: Consider both initial investment and long-term operating costs.
- Reliability and durability: Select a motor that meets the expected service life of the required application.
Reference: Introduction to Motor Technologies. Yuji Akiyama, Kogyo Chosakai Publishing Co., Ltd. 1999
-
The World’s Smallest Hollow Shaft Motor
-
Servo-drivers: How they are made and how they are used
-
Small Servo Motor for Robot Joints

-
The Story of Motor - Rule, principle and history -

-
What is a collaborative robot? An introduction to the functions and performance of collaborative robots

-
Bionic (Prosthetic) Hands and Micro-motors



